FTP, SFTP, and FTPS Transfer Guide
This guide covers the use of FTP, SFTP, and FTPS protocols for file transfers in S-Filer Portal, including SSH public key authentication for enhanced security.
Overview
S-Filer Portal supports the standard FTP, SFTP, and FTPS file transfer protocols. As a result, you can use client applications that support these protocols to access your S-Filer account and to transfer files.
The following sections describe the different communication protocols available in S-Filer Portal:
FTP Transfers
S-Filer Portal supports FTP, but we don't recommend its use: this protocol is not secure. All data---including your username, your password, and the files you transfer---are transmitted without encryption. This allows a third party "snooping" on the network to intercept them. On the other hand, you can use FTP if you are using a network that you know has been secured.
You cannot use FTP unless the S-Filer Portal administrator has configured it. By default, port 21 is used. You should check with your administrator if the default ports were used. The following example shows how to use the FTP client of Windows 7.
If your multi-protocol S-Filer server is, for example, on a machine named www.sfiler.com, you can access your S-Filer account by entering ftp://www.sfiler.com/ in the Address field of Windows Explorer. The Log On As dialog box will open:

You must enter the username and password that you use for S-Filer Portal. If your username belongs to a domain external to S-Filer Portal (such as Active Directory), add "@" and the domain name after your username. For example, if your username is jsmith and you use the okiok.com domain, then you must enter jsmith@okiok.com in the User name field.
It's very important to use the Domain name that is in the drop down list on the logon screen

It's very important to use the Domain name that is in the drop down list on the logon screen. In our case its okiok.com.
Once you login in this manner, you can access your own files as well as those of the communities to which you belong. You can upload and download these files using FTP.

Note: When using FTP, only the short name of each community appears (and not the description).
FTPS Transfers
S-Filer Portal supports FTPS, which is an FTP protocol that runs over a secure communication channel. We strongly recommend that you use FTPS rather than FTP.
You cannot use FTPS unless the S-Filer Portal administrator has configured it. By default, port 990 is used for implicit and port 21 for explicit FTP over TLS. You should check with your administrator if the default ports were used. The following example is based on FileZilla, a FTPS client for Windows. Here is how to configure a connection to the S-Filer server:

You must enter the username and password that you use for S-Filer Portal. If your username belongs to a domain external to S-Filer Portal (such as Active Directory), add "@" and the domain name after your username. For example, if your username is jsmith and you use the okiok.com domain, then you must enter jsmith@okiok.com in the User field.
Once authenticated, the user will have access to his files and those of the communities of which he is a member. It should be noted that the names of the communities used in FTPS mode are the short names of the community and not the content of the description field in the Web interface. It is now possible to send and receive files using the FTPS protocol.
Note: Check with the FTP configuration to be sure you use the correct domain name.
All FTP and FTPS transfers must use the Passive Transfer mode.
Below is an example of setting the Transfer mode to Passive for the FileZilla client

If your Inbox or community contains accented characters you should configure your FTPS client to use UTF8 to be sure the names are displayed properly.

The first time you login you will receive a warning for the FTPS certificate that S-Filer is using. You can trust this certificate and it will be the one used for all FTPS transfers.

Once you login in this manner, you can access your own files as well as those of the communities to which you belong. You can upload and download these files using FTPS.
Note: When using FTPS, only the short name of each community appears (and not the description).

SFTP Transfers
S-Filer Portal supports SFTP, which is an FTP protocol that runs over a secure SSH communication channel. We recommend that you use SFTP rather than FTP.
You cannot use SFTP unless the S-Filer Portal administrator has configured it. By default, port 22 is used. You should check with your administrator if the default port was used. The following example shows how to use the SFTP client of Windows. The following example is based on FileZilla, an SFTP client for Windows. Here is how to configure a connection to the S-Filer server:

You must enter the username and password that you use for S-Filer Portal. If your username belongs to a domain external to S-Filer Portal (such as Active Directory), add "@" and the domain name after your username. For example, if your username is jsmith and you use the Okiok.com domain, then you must enter jsmith@okiok.com in the User field.
Note: Check with the FTP configuration to be sure you use the correct domain name Figure 36 - Authentication for Active Directories Users

The first time that you connect to the S-Filer server, you will be asked to accept the S-Filer Portal key. You can trust this certificate and it will be the one used for all SFTP transfers

Note: When using SFTP, only the short name of each community appears (and not the description).

SSH Public Key Authentication
SSH public key authentication provides a more secure alternative to password-based authentication for SFTP transfers. This method uses cryptographic key pairs instead of passwords, eliminating the need to transmit passwords over the network and providing stronger security.
Prerequisites
- Access to S-Filer Portal with administrative privileges
- SSH key pair generated on the client system
- SFTP client software installed on the client system
How SSH Public Key Authentication Works
SSH public key authentication works by using a pair of cryptographic keys:
- Private key: Kept securely on the client system and never shared
- Public key: Stored on the S-Filer server and used to verify the client's identity
When a client attempts to connect via SFTP, the server uses the public key to verify that the client possesses the corresponding private key, without the private key ever being transmitted.
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Generate SSH Key Pair
On your client system, generate an SSH key pair using one of the following methods:
Using OpenSSH (Linux/macOS):
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your-email@example.com"Using PuTTYgen (Windows):
- Download and install PuTTYgen
- Click "Generate" and move your mouse to create randomness
- Save both the public and private keys
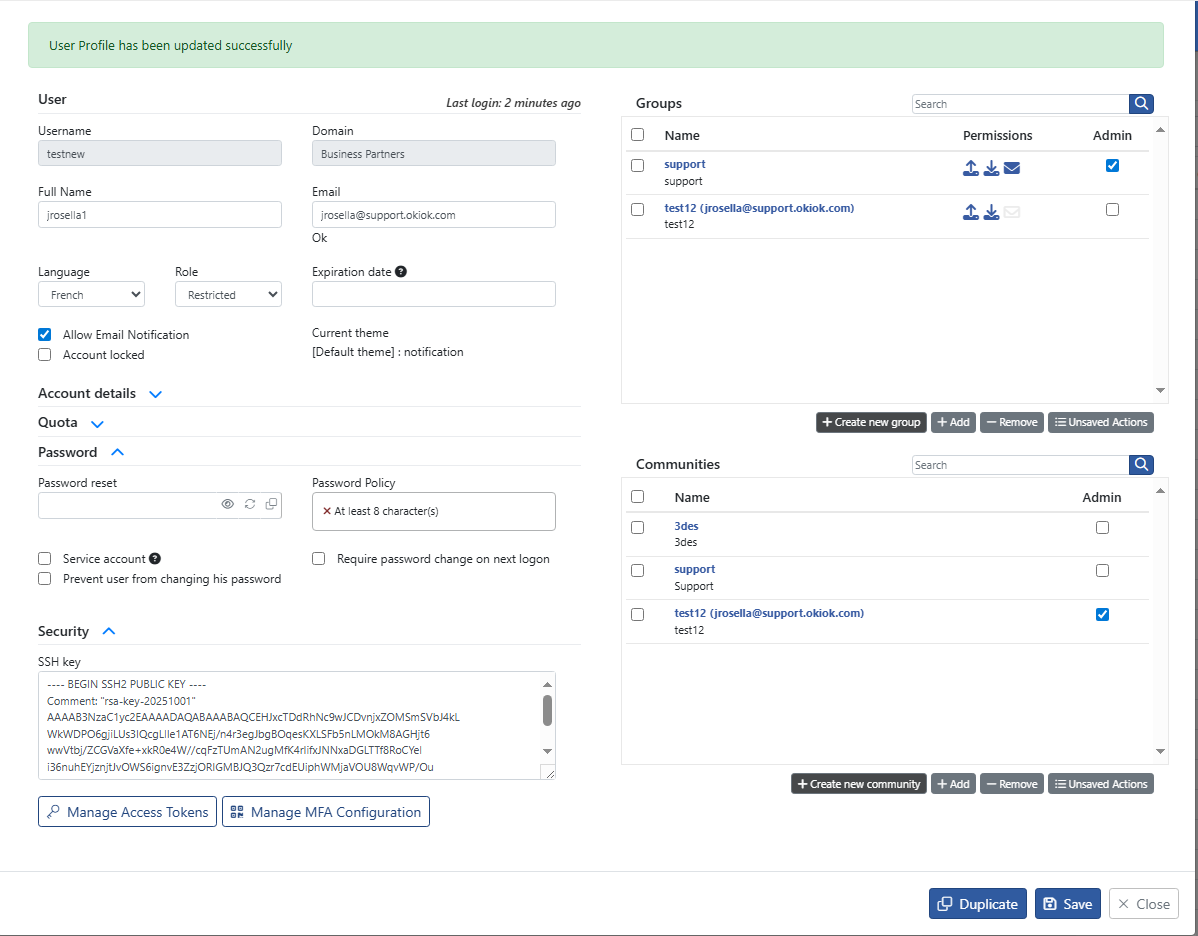
Step 2: Configure Public Key in S-Filer
- Log into S-Filer Portal as an administrator
- In the left menu, click on "Users" and select the user account which must login with the public key
- In Security → SSH Key, paste the public key content
- The public key should start with "---- BEGIN SSH2 PUBLIC KEY ----"
- Click on "Save"
Step 3: Configure SFTP Client
Configure your SFTP client to use the private key for authentication:
Using command-line SFTP:
sftp -i /path/to/private_key username@sfiler-server.comUsing FileZilla:
- Go to Edit → Settings → SFTP
- Add your private key file
- Connect using the username and server address
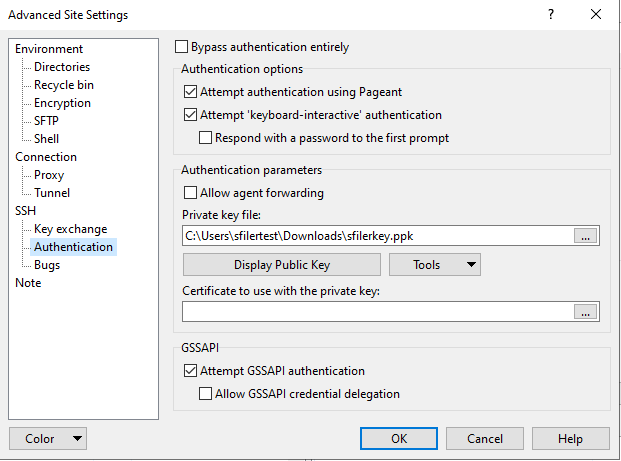
Using WinSCP on Windows:
- Open the Advanced Settings for the site
- Under SSH → Authentication
- Add your private key file
- Connect using the username and server address
Security Considerations
- Keep your private key secure and never share it
- Use strong passphrases for your private key
- Regularly rotate SSH keys
- Monitor SFTP access logs for unauthorized attempts
Troubleshooting
Common issues and solutions:
Connection refused:
- Verify the SFTP service address and port are correct. Often S-Filer is configured to use a different port than the default 22.
- Check firewall settings for the corresponding port.
Authentication failed:
- Ensure the public key is correctly added to S-Filer
- Verify the private key matches the public key
- Check file permissions on the private key (should be 600 on linux)
SFTP server asks for a password:
- Ensure the private key is correctly configured in the SFTP client
Best Practices
- Implement key rotation policies
- Monitor and log all SFTP access attempts
- Use strong encryption algorithms (RSA 4096-bit or Ed25519)
- Regularly audit SSH key usage and remove unused keys
